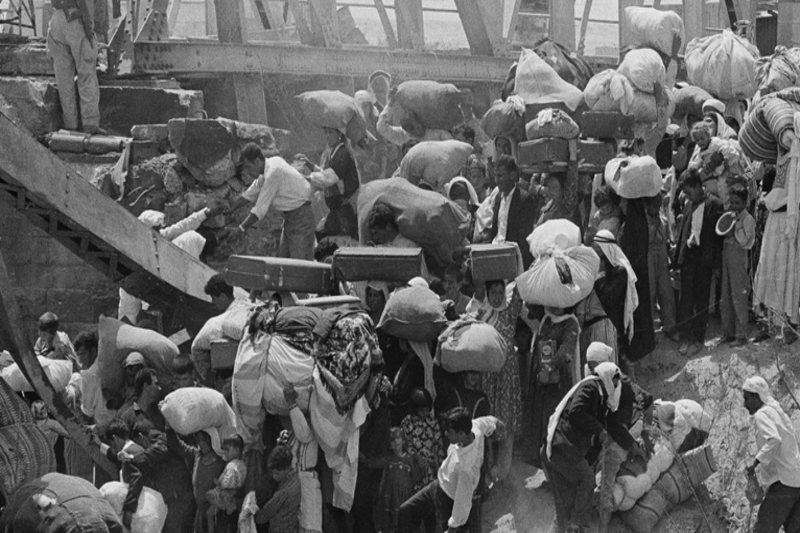
Palestinian refugees carry their belongings as they prepare to cross the wrecked Allenby Bridge over the Jordan River from the Israeli-occupied West Bank on June 22, 1967 [AP]
By Aryan D.M
"Peace is not the absence of war but the presence of justice and the absence of fear." - Shimon Peres
A Seven-Day Overview
The Israel-Hamas conflict has entered its seventh day, with no signs of de-escalation.
The situation in the region is dire, marked by intense fighting, significant human impact, and a complex web of international reactions and diplomacy.
Fighting Intensifies
Israeli Airstrikes in Gaza: Israel has carried out intense airstrikes, targeting what they claim are 750 "military targets" in the densely populated Gaza Strip, including 12 high-rise buildings. This has raised concerns about civilian casualties and infrastructure damage.
Imminent Ground Invasion: There are ominous signs of an Israeli ground invasion of Gaza, expected to start over the weekend, and this operation is anticipated to result in heavy casualties.
Horrifying Hamas Atrocities: US Secretary of State Antony Blinken was shown graphic images of Hamas atrocities, including a baby riddled with bullets and beheaded soldiers, intensifying global outrage.
Hamas Calls for Uprising: Gaza's ruling Hamas has called on Palestinians to protest against Israel's bombardment by marching to East Jerusalem's Al-Aqsa Mosque, creating a highly volatile situation.
Global Escalation: Anti-Jewish attacks are surging globally, with anti-Jewish protests banned in France and Germany. England and France have reported a significant number of attacks against Jews, and even China experienced an attack on a Jewish diplomat. In the US, white supremacists are joining pro-Palestine movements, further complicating the international response.
Attacks Across the Globe
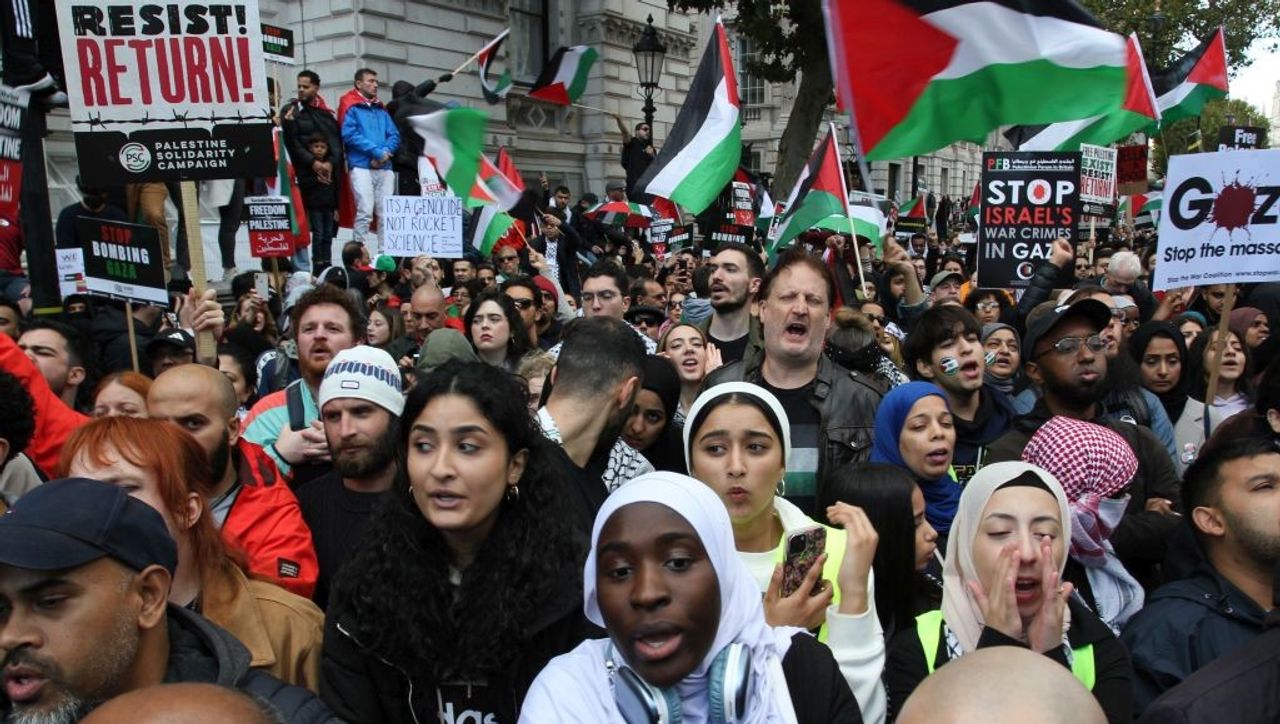

Over 150,000 people protested in central London Saturday to demand an end to Israel’s war on the Palestinians.
France: Anti-Jewish protests have been banned in France, which recently witnessed approximately 100 attacks against Jewish individuals within a single week, underscoring the magnitude of the challenge.
Germany: In Germany, anti-Jewish protests have also been banned as part of the response to the escalating tensions.
England: England, in a span of just one week, recorded an alarming 89 attacks against Jews, necessitating tightened security measures.
China: A Jewish diplomat faced an alarming attack in China, highlighting the global repercussions of the conflict.
United States: In the United States, an alarming trend has seen white supremacists aligning with pro-Palestinian causes, adding a dangerous dimension to the global response.
Expanding Conflict
Israel's actions have triggered regional repercussions, including airstrikes on Aleppo and Syrian airports in response to intelligence reports of Iranian military aid reaching Hamas.
Hezbollah has issued severe warnings against Israel and initiated attacks in northern Israel, further escalating the conflict.
The West Bank has also witnessed violent protests with three casualties.
Humanitarian Crisis
Humanitarian Crisis Looms: The United Nations has warned of a devastating humanitarian crisis, particularly in northern Gaza, as Israel has called for its depopulation. The UN "considers it impossible for the relocation to take place without devastating humanitarian consequences."
Mounting Casualties: Israel has reported over 1,300 deaths and at least 3,000 wounded. Meanwhile, Gaza authorities claim that over 6,000 Palestinians have been killed, with more than 6,000 wounded, highlighting the scale of the human tragedy.
Global Responses and Diplomatic Efforts:
UK Support for Israel: The United Kingdom is deploying two Royal Navy ships and surveillance aircraft to the eastern Mediterranean to support Israel and reinforce regional stability.
US Involvement: US Secretary of State Antony Blinken's visit to the region signals a diplomatic effort. He is set to meet with King Abdullah II of Jordan and Palestine's President Mahmoud Abbas, underscoring the urgency of the situation.
Turkish Call for Palestinian State: Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has urged the establishment of a sovereign Palestinian state as a lasting solution to the conflict, contributing to the discussion of potential resolutions.
Global Protests: Pro-Palestinian rallies have erupted worldwide, with some leading to confrontations with law enforcement. France used tear gas and water cannon to disperse a banned rally in support of the Palestinian people, highlighting the global impact of the conflict.
Hezbollah-Iran Meeting and Escalation Warning: In a recent meeting, Hezbollah leaders and Iranian officials explored scenarios for a full-scale military intervention in Israel. Iran's foreign minister issued a stern warning, stating that Israel would bear the responsibility for potential consequences if they continued actions deemed detrimental to Palestinians. This situation raises concerns about regional escalation.
Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: Historical Roots
Introduction
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has deep historical roots dating back to the aftermath of World War I. The British mandate over Palestine, established through the Balfour Declaration, sowed the seeds of discord between the Jewish and Arab communities.
The 1947 UN partition plan, which was accepted by Jewish leaders but rejected by the Arabs, further exacerbated tensions.
The 1948 declaration of the State of Israel led to a war with neighboring Arab nations and the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians.
These historical grievances continue to fuel the conflict.
Historical Context
The British Mandate over Palestine:
To understand the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, it's essential to delve into its historical context. The conflict's origins can be traced to the aftermath of World War I when the British Empire gained control over Palestine. The Balfour Declaration of 1917, a letter from British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour to Lord Rothschild, expressed British support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine.
The 1947 UN Partition Plan:
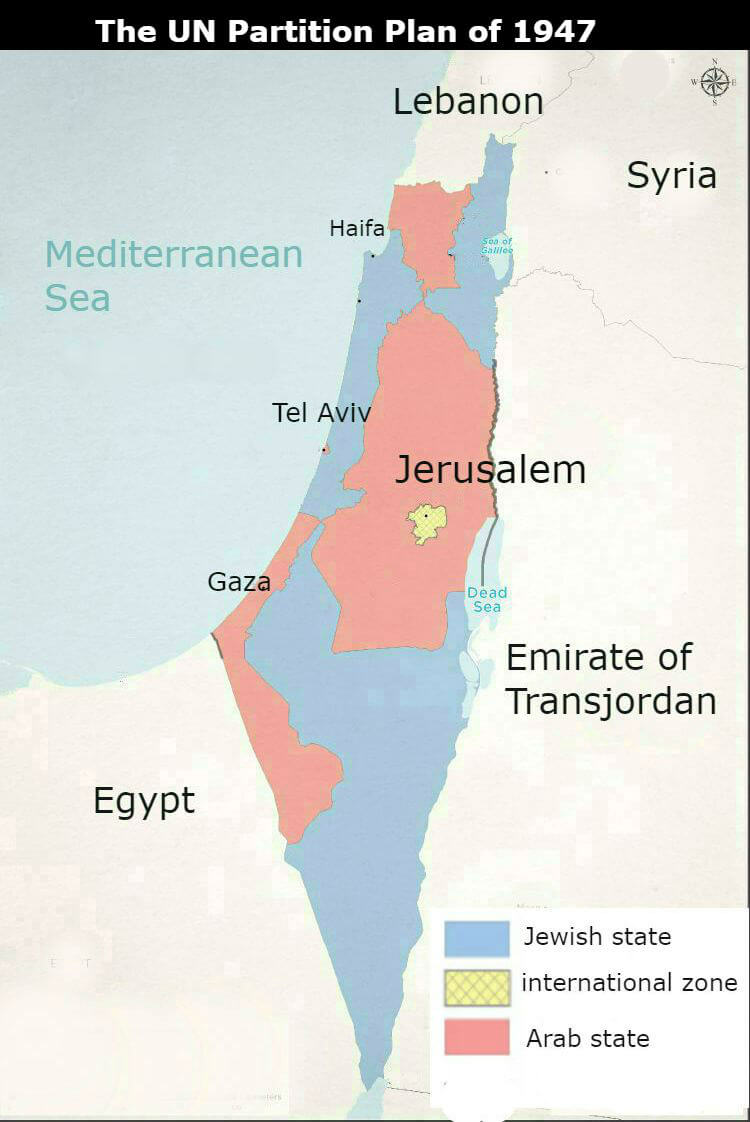
As tensions between Jewish immigrants and the Arab population in Palestine grew, the United Nations proposed a partition plan in 1947. The plan sought to divide Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem under international administration. While Jewish leaders accepted the plan, Arab leaders rejected it, leading to further hostilities.
The 1948 War and Palestinian Displacement:
On May 14, 1948, David Ben-Gurion declared the establishment of the State of Israel. This declaration was met with immediate opposition from neighboring Arab countries, leading to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
The Role of Hamas
Hamas, founded in 1987, has played a significant role in the ongoing conflict.
The group's military wing, the Ezzedine al-Qassam Brigades, recently launched over 5,000 rockets into Israel, driven by their perception of Israeli occupation and aggression.
Hamas's role is contentious, with some viewing them as freedom fighters and others as terrorists due to their use of violence against civilians.
Despite international attempts to broker peace, a lasting resolution remains elusive.
The Recent Escalation
Impending Catastrophe: On the Brink of War:
The recent escalation in violence has brought the Israeli-Palestinian crisis to the brink of a potentially devastating situation.
Thousands of rockets have rained down on Israel from Gaza, prompting Israeli authorities to declare a "State of War" and urge citizens to seek shelter.
The situation is deeply concerning, as it has already resulted in casualties on both sides and threatens to escalate into a full-blown war.
Hamas has asserted that its actions are a response to what they perceive as Israeli crimes and occupation.
In contrast, Israel maintains that it has the inherent right to defend itself against rocket attacks and to protect the safety of its citizens.
This cycle of violence has once again brought the Israeli-Palestinian conflict to the forefront of international attention, with global leaders calling for restraint and a peaceful resolution.
In light of the historical context and ongoing tensions, it's important to examine the numerous attempts made to bring about peace in the region. Here are some key milestones in these diplomatic efforts.
The recent escalation, deeply rooted in the historical context, brings us to a critical juncture where we must explore the various attempts made to achieve peace over the decades.
Subsequent Peace Attempts and Agreements
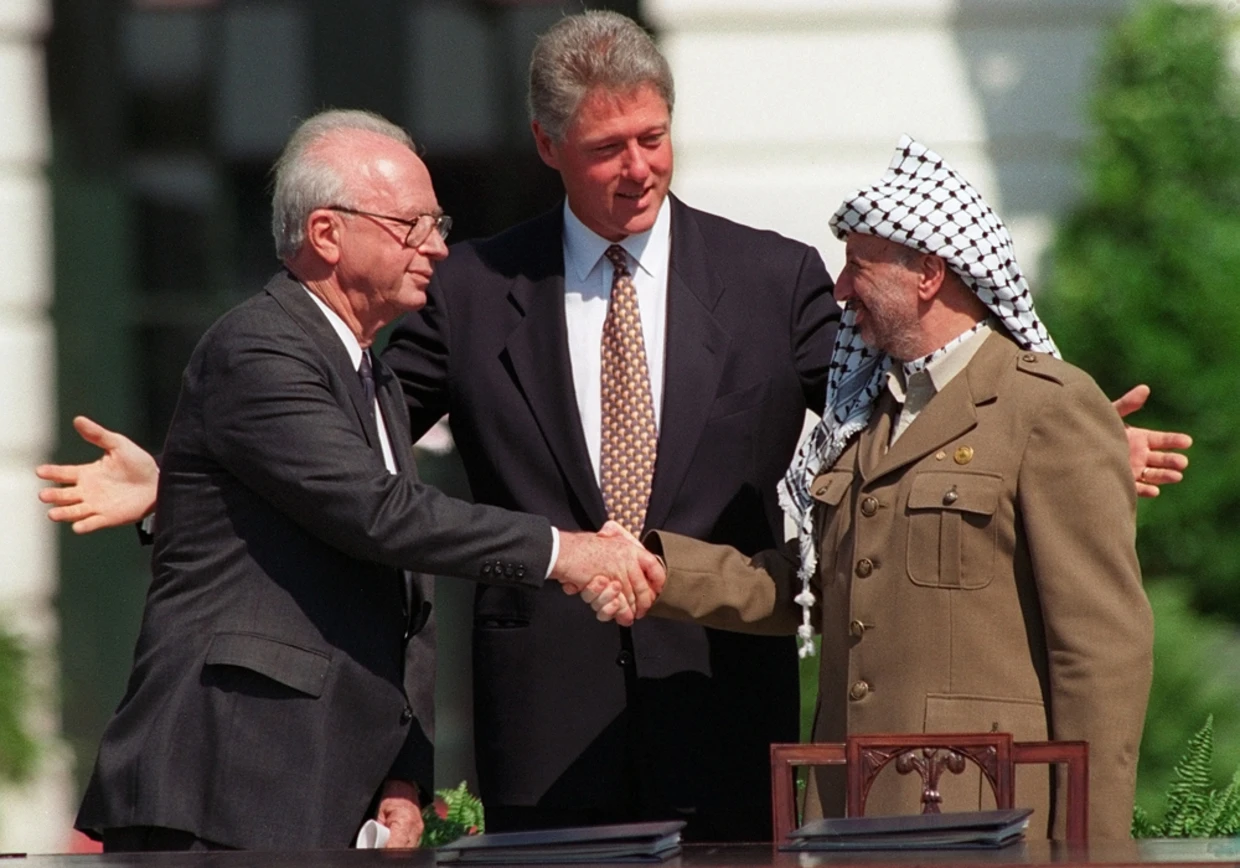

Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin (L) and PLO Chairman Yasser Arafat (R) shake hands as US President Bill Clinton watches after the signing of the Oslo Accords at the White House in Washington, Sept. 13, 1993. - Reuters/Gary Hershorn
In the decades following the establishment of Israel, numerous attempts were made to bring about peace in the region. These efforts included diplomatic negotiations, peace agreements, and international mediations. Here are some key milestones:
Camp David Accords (1978): The Camp David Accords were signed between Egypt and Israel, with the United States as a mediator. These agreements led to the normalization of relations between Egypt and Israel and marked the first time an Arab country officially recognized Israel.
Oslo Accords (1993): The Oslo Accords were a significant breakthrough, with the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) recognizing Israel's right to exist and Israel recognizing the PLO as the representative of the Palestinian people. The accords established the Palestinian Authority and outlined a framework for Palestinian self-governance in parts of the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
Camp David Summit (2000): A summit hosted by the United States between Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak and Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat aimed to address the core issues of the conflict, including borders, refugees, and Jerusalem. Unfortunately, the summit ended without a final agreement.
The Road Map for Peace (2003): Proposed by the Quartet on the Middle East (the United States, European Union, United Nations, and Russia), the Road Map outlined a series of steps toward a two-state solution. However, implementation faced significant challenges.
Annapolis Conference (2007): This conference brought together Israeli and Palestinian leaders, with the goal of reaching a peace agreement. While discussions were held, no final agreement was reached.
Gaza War and Ceasefire (2008-2009): Following the Annapolis Conference, a major conflict erupted between Israel and Hamas in Gaza. It culminated in Operation Cast Lead, a three-week military campaign by Israel. While this was not a peace attempt, it did lead to a ceasefire brokered by Egypt and coordinated with international actors.
Direct Negotiations (2010): In 2010, there was an attempt to restart direct negotiations between Israel and the Palestinian Authority, mediated by the United States. However, these talks quickly broke down over issues related to Israeli settlements in the West Bank.
2013-2014 Peace Talks: U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry led another effort to revive peace talks between Israel and Palestine in 2013. The negotiations continued for several months but ultimately collapsed in April 2014.
2018 U.S. Peace Plan: In January 2018, the United States, under the Trump administration, unveiled a peace plan known as the "Deal of the Century." The plan proposed a two-state solution but was met with strong opposition from Palestinians, who felt it heavily favored Israel. It did not lead to renewed negotiations.
Normalization Agreements (2020): While not a comprehensive peace agreement, the Abraham Accords, brokered by the United States, saw Israel normalize diplomatic relations with the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Bahrain, Sudan, and Morocco in 2020. These agreements focused on economic and security cooperation but did not directly address the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Recent Developments (2021-2022): Following the 11-day conflict in May 2021 between Israel and Hamas in Gaza, there have been various efforts to achieve a ceasefire and humanitarian assistance for Gaza. Diplomatic efforts, including those involving Egypt and Qatar, have aimed to maintain stability in the region.
Global Implications
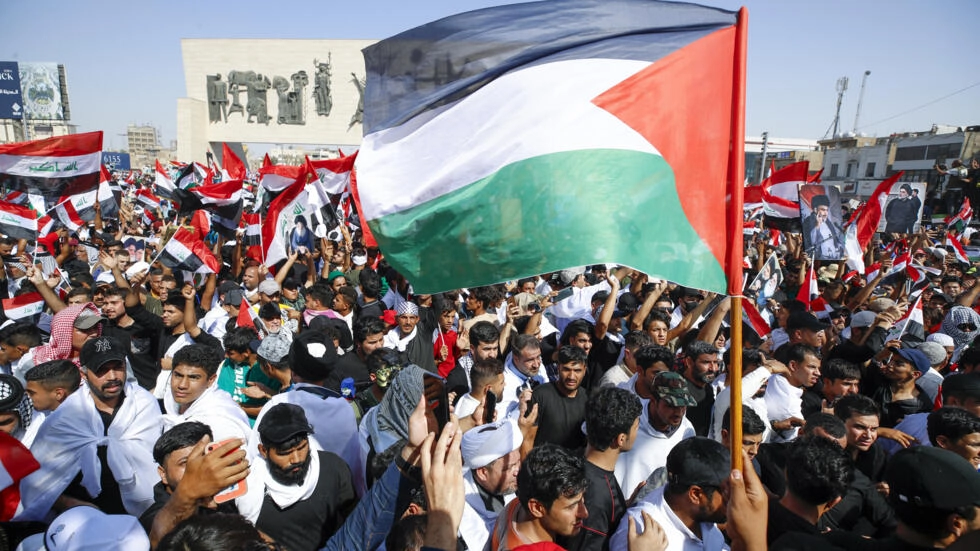

Protesters wave a Palestinian flag at a rally in Baghdad's Tahrir Square on October 13 (Photo: Ahmad AL-RUBAYE / AFP)
Explosive Regional Fallout:
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has historically served as a volatile flashpoint in the Middle East, with far-reaching implications that extend beyond the borders of Israel and Palestine.
As recent tensions have escalated, there is growing concern about the potential ripple effects on neighboring states and the instructive parallels that can be drawn with the ongoing Russia-Ukraine War.
In the Middle East, instability in one region often has a domino effect, impacting the delicate geopolitical balance of the entire area.
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has the potential to exacerbate existing tensions and trigger new conflicts.
It can inflame anti-Israel sentiment among neighboring countries and radicalize segments of their populations, leading to political unrest and even acts of violence.
Furthermore, parallels with the Russia-Ukraine War are worth noting.
Both conflicts involve territorial disputes, ethnic tensions, and external actors with vested interests.
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict serves as a reminder of the challenges in resolving deeply rooted disputes and the potential for external powers to exacerbate conflicts rather than mediate them.
Regional Powder Keg: The Domino Effect
The Middle East, a region marked by longstanding instability and conflicts, faces the risk of profound consequences due to an escalation in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
This potential escalation raises significant concerns, particularly in Lebanon, where Hezbollah, a Shiite militant group closely allied with Hamas, holds a substantial presence.
Lebanon's existing sectarian divisions and historical grievances have already created a fragile peace, and an intensification of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict could fuel anti-Israel sentiment among Hezbollah supporters, potentially pushing the group to become more involved.
This could further destabilize Lebanon, and the repercussions might extend well beyond its borders, sending shockwaves throughout the region.
Furthermore, an escalation in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict could strain relations with Egypt and Jordan, both of which have historically upheld peace agreements with Israel.
These treaties, the Camp David Accords with Egypt in 1978 and the Jordan-Israel Peace Treaty in 1994, have played pivotal roles in maintaining regional stability.
Any deterioration in these relationships could disrupt the delicate balance of power in the Middle East.
Egypt, with its population's historical support for the Palestinian cause, could experience internal tensions, potentially leading to protests and political unrest.
Such an escalation could also complicate Egypt's role as a mediator between the conflicting parties.
Similarly, Jordan, acting as a buffer state and a mediator in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, might face domestic pressure due to its significant Palestinian population.
Instability within Jordan would not only affect its internal stability but also undermine its role as a stabilizing force in the region.
In conclusion, the potential escalation of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict carries the grave risk of disrupting the already fragile stability in the Middle East.
This could result in heightened tensions, possible clashes, and the destabilization of neighboring countries such as Lebanon, Egypt, and Jordan.
The complex web of regional dynamics emphasizes the urgent need for a peaceful resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian crisis to prevent further regional instability and conflict.
The global implications of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict extend beyond the region's borders. Understanding these global implications leads us to examine the complex alliances and influences at play.
Global Alliances and Influences
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict's enduring nature and its ability to shape global alliances is indeed a testament to its complexity and significance in Middle Eastern geopolitics.
Iran's longstanding support for Hamas, a Palestinian militant group, has put it at odds with Israel, a close ally of the United States. This ideological and strategic divide has not only fueled regional tensions but has also influenced broader global alliances.
The United States, a staunch supporter of Israel, has consistently provided military aid and diplomatic backing to the Israeli government. This unwavering commitment has made it a key player in the conflict and has driven a wedge between the U.S. and countries like Iran, which view Israel as a regional adversary.
As the Israeli-Palestinian conflict escalates, it has the potential to further strain relations between the United States and Iran, leading to a more confrontational stance in an already volatile region.
This escalation could trigger a ripple effect, with other countries in the Middle East, such as Saudi Arabia and Turkey, also aligning themselves based on their positions regarding the conflict. Such a scenario has the potential to intensify existing regional rivalries and security threats.
The conflict's international reverberations extend far beyond the Middle East, with European nations often being divided in their approach.
While some countries, like the United Kingdom and Germany, have strong ties with Israel and tend to support its actions, others, like France, have traditionally leaned towards a more balanced or pro-Palestinian stance.
These differing viewpoints have the potential to create divisions within the European Union and impact its collective foreign policy.
Additionally, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict has gained significant attention in international forums, particularly at the United Nations.
It has consistently been a subject of debate and resolutions, reflecting the global community's concerns about the humanitarian impact of the conflict and the need for a peaceful resolution.
In conclusion, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict's enduring nature and the global alliances and influences it shapes underline the complex dynamics at play.
The conflict has become more than a regional dispute; it has global implications that impact major players like the United States and Iran and contribute to diplomatic divisions worldwide.
Key Obstacles to PeaceTerritorial Disputes: The conflicting claims over territory, particularly in the West Bank, including the status of Israeli settlements, continue to be a significant obstacle to peace.Status of Jerusalem: The status of Jerusalem is a deeply contentious issue, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming it as their capital. Resolving this issue remains challenging.
Right of Return: The Palestinian demand for the right of return for refugees and their descendants who were displaced in the 1948 war is a persistent obstacle in negotiations.
Security Concerns: Ensuring the security of both Israelis and Palestinians is a major concern. The fear of terrorism and violence shapes security-related negotiations.
Hamas and Palestinian Political Division: The division between the Palestinian Authority and Hamas complicates efforts for a unified Palestinian leadership, making negotiations more challenging.
Regional and International Actors
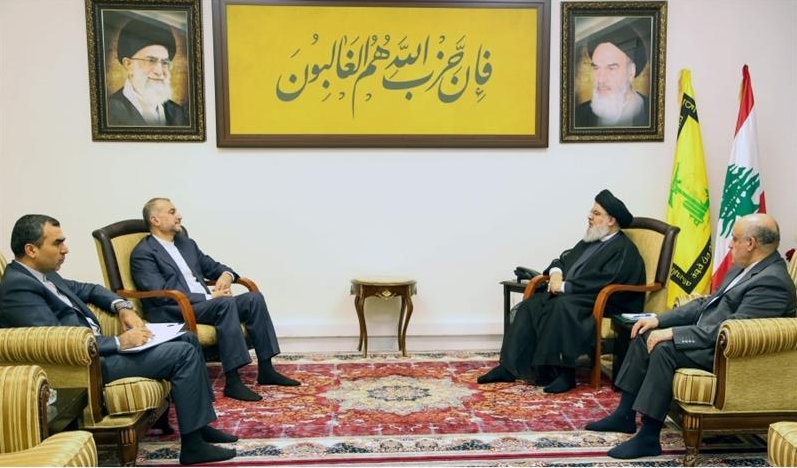

This handout picture provided by Hezbollah s media office on October 13, 2023, shows the Lebanese Shia group s secretary general, Hassan Nasrallah (2nd-R) meeting with Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian (2nd-L) at an undisclosed location in Lebanon. AFP
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is further complicated by the involvement of regional and international actors. Iran's support for groups like Hamas, along with its anti-Israel stance, adds complexity to the situation.
The presence of Hezbollah in Lebanon, closely aligned with Iran, introduces the potential for further escalation.
Syria's enduring conflict with Israel over the Golan Heights and its support for Palestinian groups remain ongoing sources of tension.
Russia's interest in diverting attention from the Ukraine war may shape its approach to the conflict, potentially influencing international discourse.
Meanwhile, China's strategic interests in the Middle East, particularly concerning its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and regional stability, have the potential to impact the peace process on a global scale.
These various actors contribute to the multifaceted nature of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Potential Paths to PeaceTwo-State Solution: The most commonly discussed path to peace involves the creation of two states, Israel and Palestine, living side by side with recognized borders.
One-State Solution: Some advocate for a single, democratic state that includes both Israelis and Palestinians with equal rights. However, this is a contentious proposal.
Incremental Approaches: Gradual progress on specific issues, such as borders and security, can build confidence and lead to a comprehensive solution over time.
Regional Involvement: Engaging neighboring Arab states, such as Jordan and Egypt, in the peace process can provide a broader framework for resolution.
Grassroots Initiatives: People-to-people initiatives, involving civil society and grassroots movements, can foster understanding and reconciliation at the community level.
A Time for Diplomacy
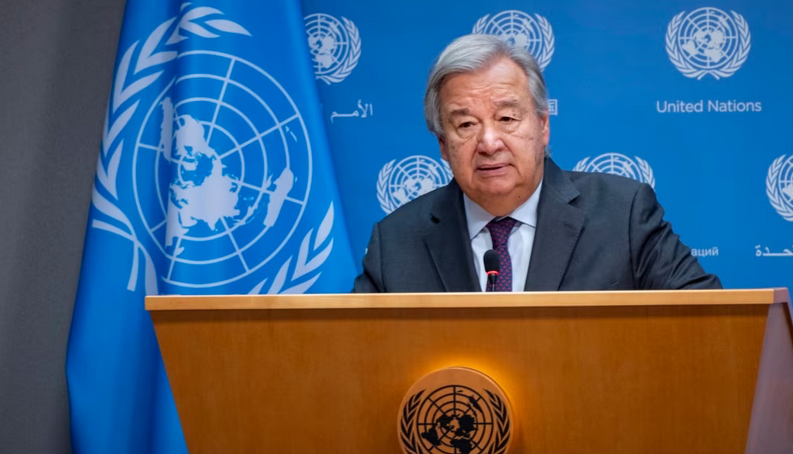

United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres appealed to the parties in the Middle East to prevent a spillover of the current conflict. (Photo: AP)
In the midst of the ongoing conflict and escalating tensions, the imperative for diplomatic efforts is greater than ever.
While there is no easy fix to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the history of peace negotiations and agreements underscores the importance of dialogue and negotiation in seeking a lasting resolution.
Diplomatic efforts should encompass the following key principles:
Immediate Ceasefire: The priority should be to halt the violence and minimize civilian casualties. A ceasefire, recognized and respected by all parties involved, is essential to create a conducive environment for negotiations.
Resumption of Direct Talks: A renewed commitment to direct talks between Israeli and Palestinian leadership is critical. These negotiations should address the core issues, Hostages, borders, the status of Jerusalem, refugees, and security.
Involvement of International Mediators: The participation of international mediators, such as the United Nations, the United States, the European Union, and the Arab League, can facilitate negotiations and lend credibility to the process.
Humanitarian Aid and Reconstruction: The urgent humanitarian needs of those affected by the conflict must be addressed. This includes providing aid to Gaza, rebuilding infrastructure, and ensuring access to healthcare, education, and basic services.
Diplomatic Pressure: The international community, through diplomatic means, should exert pressure on all parties to engage in constructive dialogue and adhere to agreements. Sanctions and incentives can be used judiciously to encourage compliance.
Addressing Root Causes: Efforts should be made to address the root causes of the conflict, including grievances, historical injustices, and socioeconomic disparities. This may involve programs focused on economic development, education, and conflict resolution.
Cultivating Grassroots Peace Initiatives: Engaging civil society, non-governmental organizations, and grassroots movements can help build support for peace and bridge divides between communities.
The path to a lasting resolution is fraught with challenges, but history has shown that dialogue and diplomacy, coupled with international support, offer the best chance for a peaceful future.
The human toll of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is immeasurable, and the suffering on both sides must end.
Now, more than ever, is the time to work toward a just and enduring solution to this protracted conflict.
In conclusion, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, with its deep historical roots and the recent escalation, carries profound implications for the region and the world.
The enduring nature of the conflict underscores the need for renewed diplomatic efforts and international cooperation to seek a peaceful resolution.
The human cost of the conflict demands nothing less.
Related News:
Israel’s Intelligence Failure and the Hamas Attack: An In-Depth Analysis - (Aryan D.M.)


















